library(tidyverse) # data wrangling and cleaning
library(tidymodels) # modeling and machine learning
library(palmerpenguins) # penguin dataset
library(gt) # creating table objects for data
library(ranger) # random forest model engine
library(brulee) # neural network with torch
library(pins) # sharing resources across sessions & users
library(vetiver) # model versioning and deployment
library(plumber) # API creation
library(conflicted) # handling function conflicts
tidymodels_prefer() # handle common conflicts with tidymodels
conflict_prefer("penguins", "palmerpenguins")
options(tidymodels.dark = TRUE) # dark mode console messagesMLOps in R: The Whole Game
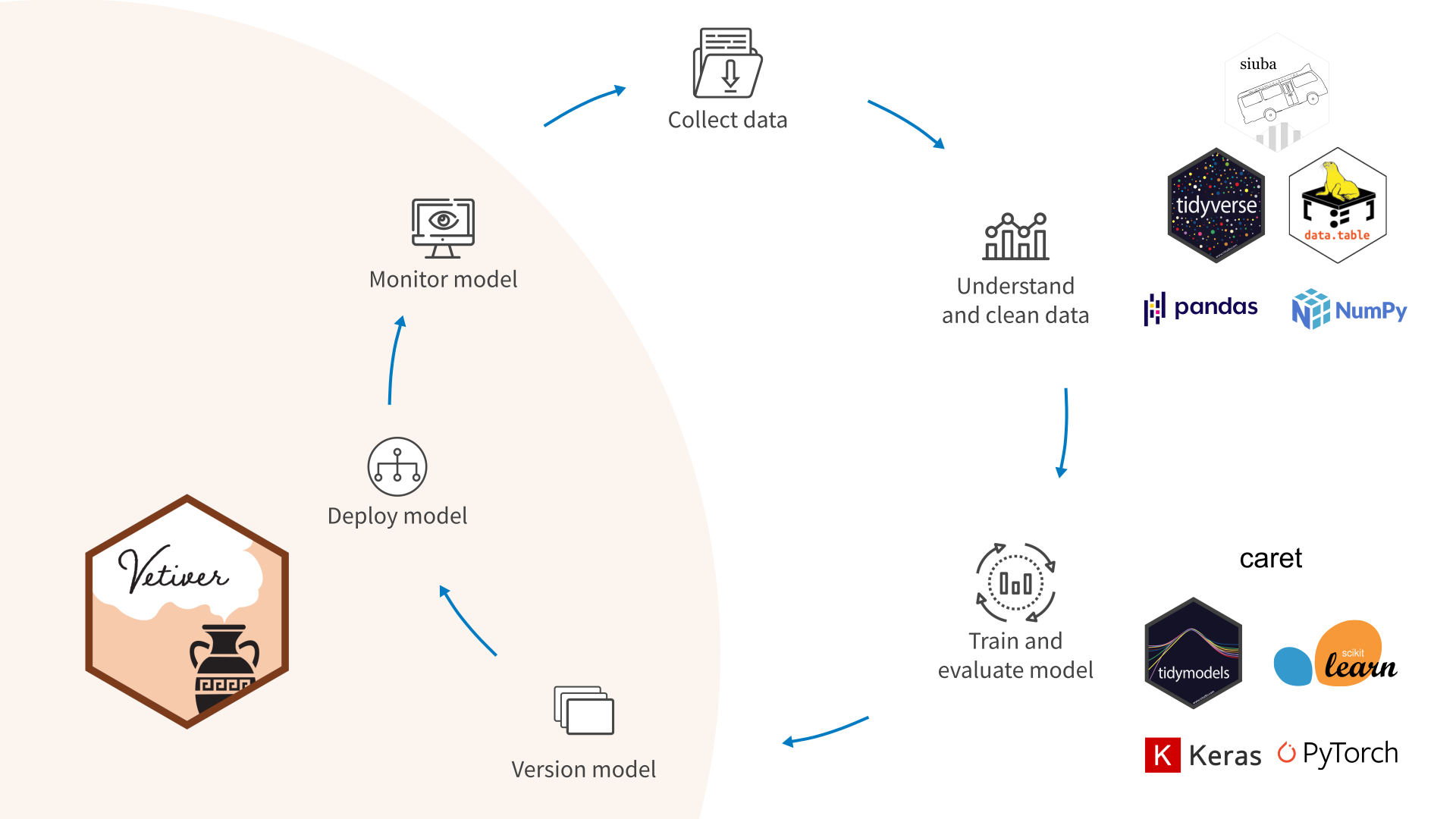
Source: MLOPs with vetiver
Load Packages & Set Options
Exploratory Data Analysis
Note: You should do more exploration than this for a new set of data.
Exploratory Data Analysis
Note: You should do more exploration than this for a new set of data.

Prepare & Split Data
# remove rows with missing sex, exclude year and island
penguins_df <-
penguins |>
drop_na(sex) |>
select(-year, -island)
# set the seed for reproducibility
set.seed(1234)
# Split the data into train and test sets stratified by sex
penguin_split <- initial_split(penguins_df, strata = sex)
penguin_train <- training(penguin_split)
penguin_test <- testing(penguin_split)
# create folds for cross validation
penguin_folds <- vfold_cv(penguin_train)Create Recipe
See the getting started page from the {recipes} pkgdown site to learn more. You can also learn more about the recommended ordering of steps.
penguin_rec <-
recipe(sex ~ ., data = penguin_train) |>
step_YeoJohnson(all_numeric_predictors()) |>
step_dummy(species) |>
step_normalize(all_numeric_predictors())- 1
- Define the recipe on the training data with sex as the target and all other vars as predictors
- 2
- Apply Yeo-Johnson transformation to all numeric predictors for skewness
- 3
-
Create dummy variables for nominal variable
species - 4
- Normalize all numeric predictors
Specify Models with {parsnip}
Logistic Regression
Specify Models with {parsnip}
Neural Network with {torch}
Fit Models & Tune Hyperparameters
Use Bayes optimizaiton for hyperparameter tuning
Fit Models & Tune Hyperparameters
Use {workflowsets} to fit all three model types with hyperparameter optimization for random forest and neural net models.
Compare Model Results
Tabular view
# create table of best models defined using roc_auc metric
rank_results(workflow_set,
rank_metric = "roc_auc",
select_best = TRUE) |>
gt()| wflow_id | .config | .metric | mean | std_err | n | preprocessor | model | rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| recipe_torch | Iter30 | accuracy | 0.8998333 | 0.01903287 | 10 | recipe | mlp | 1 |
| recipe_torch | Iter30 | roc_auc | 0.9791730 | 0.01022562 | 10 | recipe | mlp | 1 |
| recipe_glm | Preprocessor1_Model1 | accuracy | 0.8998333 | 0.01994506 | 10 | recipe | logistic_reg | 2 |
| recipe_glm | Preprocessor1_Model1 | roc_auc | 0.9686469 | 0.01234732 | 10 | recipe | logistic_reg | 2 |
| recipe_tree | Iter2 | accuracy | 0.9118333 | 0.02512248 | 10 | recipe | rand_forest | 3 |
| recipe_tree | Iter2 | roc_auc | 0.9672987 | 0.01320487 | 10 | recipe | rand_forest | 3 |
Compare Model Results
Plotting performance

Finalize Fit
# select best model
best_fit <-
workflow_set |>
extract_workflow_set_result(best_model_id) |>
select_best(metric = "accuracy")
# create workflow for best model
final_workflow <-
workflow_set |>
extract_workflow(best_model_id) |>
finalize_workflow(best_fit)
# fit final model with all data
final_fit <-
final_workflow |>
last_fit(penguin_split)Final Fit Metrics
Final Fit Metrics

Create Vetiver Model & API
Create a vetiver model from final fit
final_fit_to_deploy <- final_fit |> extract_workflow()
v <- vetiver_model(final_fit_to_deploy, model_name = "penguins_model")
model_board <- board_folder(path = "pins-r", versioned = TRUE)
model_board |> vetiver_pin_write(v)
model_board |>
vetiver::vetiver_write_plumber("penguins_model")
write_board_manifest(model_board)- 1
-
We need to modify the
plumber.Rfile to work with a HuggingFace deployment. - 2
- The manifest is what allows us to use a GitHub repo to store our model board.
Create Vetiver Model & API
Use board_url() to store our model in a GitHub repo.
Note: For this to work, we first must push our changes to our GitHub repo.
Plumber API
Original Plumber File
# Generated by the vetiver package; edit with care
library(pins)
library(plumber)
library(rapidoc)
library(vetiver)
# Packages needed to generate model predictions
if (FALSE) {
library(parsnip)
library(recipes)
library(stats)
library(workflows)
}
b <- board_folder(path = "pins-r")
v <- vetiver_pin_read(b, "penguins_model", version = "20230730T172358Z-54641")
#* @plumber
function(pr) {
pr |> vetiver_api(v)
}Plumber API
Updated Plumber File
# Generated by the vetiver package; edit with care
library(pins)
library(plumber)
library(rapidoc)
library(vetiver)
# Packages needed to generate model predictions
if (FALSE) {
library(parsnip)
library(recipes)
library(stats)
library(workflows)
}
pin_loc <- pins:::github_raw("JamesHWade/r-mlops/main/pins-r/_pins.yaml")
b <- board_url(pin_loc)
v <- vetiver_pin_read(b, "penguins_model")
#* @plumber
function(pr) {
pr |> vetiver_api(v)
}Write Dockerfile
Original Dockerfile
# Generated by the vetiver package; edit with care
FROM rocker/r-ver:4.3.1
ENV RENV_CONFIG_REPOS_OVERRIDE https://packagemanager.rstudio.com/cran/latest
RUN apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
libcurl4-openssl-dev \
libicu-dev \
libsodium-dev \
libssl-dev \
make \
zlib1g-dev \
&& apt-get clean
COPY vetiver_renv.lock renv.lock
RUN Rscript -e "install.packages('renv')"
RUN Rscript -e "renv::restore()"
COPY plumber.R /opt/ml/plumber.R
EXPOSE 8000
ENTRYPOINT ["R", "-e", "pr <- plumber::plumb('/opt/ml/plumber.R'); pr$run(host = '0.0.0.0', port = 8000)"]Write Dockerfile
Updated Dockerfile
# Generated by the vetiver package; edit with care
FROM rocker/r-ver:4.3.1
# Create a non-root user to run the application
RUN useradd --create-home appuser
ENV RENV_CONFIG_REPOS_OVERRIDE=https://packagemanager.rstudio.com/cran/latest
ENV HOME=/home/appuser
WORKDIR $HOME
RUN apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
libcurl4-openssl-dev \
libicu-dev \
libsodium-dev \
libssl-dev \
make \
zlib1g-dev \
&& apt-get clean
COPY vetiver_renv.lock renv.lock
# Create the .cache directory and give appuser permission to write to it
RUN mkdir -p /home/appuser/.cache && chown -R appuser:appuser /home/appuser/.cache
# Create the .cache/pins/url directory and give appuser permission to write to it
RUN mkdir -p /home/appuser/.cache/pins/url && chown -R appuser:appuser /home/appuser/.cache/pins/url
RUN Rscript -e "install.packages('renv')"
RUN Rscript -e "renv::restore()"
COPY plumber.R /opt/ml/plumber.R
EXPOSE 7860
ENTRYPOINT ["R", "-e", "pr <- plumber::plumb('/opt/ml/plumber.R'); pr$run(host = '0.0.0.0', port = 7860)"]API Deployment
Required files:
vetiver_renv.lockplumber.RDockerfile
Here is an example deployment example hosted on HuggingFace Spaces.
Model Usage
A minimal shiny app to use the deployed model API
library(shiny)
library(bslib)
library(vetiver)
endpoint <-
vetiver_endpoint("https://jameshwade-penguins-model.hf.space/predict")
ui <- bslib::page_sidebar(
sidebar = sidebar(
selectInput("species", "Select Species",
choices = c("Adelie", "Chinstrap", "Gentoo")),
sliderInput("bill_length_mm", "Enter Bill Length (mm):",
min = 30, max = 60, step = 0.5, value = 45),
sliderInput("bill_depth_mm", "Enter Bill Depth (mm):",
min = 10, max = 22, step = 0.5, value = 15),
sliderInput("flipper_length_mm", "Enter Flipper Length (mm):",
min = 170, max = 235, step = 0.5, value = 200),
sliderInput("body_mass_g", "Enter Body Mass (g):",
min = 2700, max = 6300, step = 10, value = 3500),
actionButton("predict", "Predict"),
open = TRUE
),
verbatimTextOutput("info")
)
server <- function(input, output, session) {
observe({
new_data <- data.frame(
species = input$species,
bill_length_mm = input$bill_length_mm,
bill_depth_mm = input$bill_depth_mm,
flipper_length_mm = input$flipper_length_mm,
body_mass_g = input$body_mass_g
)
prediction <- predict(endpoint, new_data)
output$info <- renderPrint(prediction)
}) |> bindEvent(input$predict)
}
shinyApp(ui, server)Model Monitoring
This a bit of a contrived example but shows you the idea.
set.seed(1234)
# add observation date to training data
penguin_train_by_date <-
penguin_train |>
rowwise() |>
mutate(date_obs = Sys.Date() - sample(4:10, 1)) |>
ungroup() |>
arrange(date_obs)
# compute metrics on training data by date
original_metrics <-
augment(v, penguin_train_by_date) |>
vetiver_compute_metrics(
date_var = date_obs,
period = "day",
truth = "sex",
estimate = ".pred_class"
)Model Monitoring
This a bit of a contrived example but shows you the idea.

What could I improve?
- A less bloated vetiver_renv.lock
- Plumber and Dockerfiles that work out of the box
- Implement model monitoring